Introduction
The global sports betting market has seen explosive growth in recent years, fueled by the rise of online gambling platforms, increased internet access and penetration, and the legalization of betting in numerous countries. As of 2023, research showed that the global sports betting market was valued at around $92.1 billion, with projections suggesting it could exceed $182.1 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.3%. This market includes various betting activities, from traditional sports like soccer and horse racing to esports and virtual games.
However, the rapid expansion of the betting industry has also attracted fraudulent activity. Fraudsters actively seek to exploit weaknesses in the bookmakers’ odds-setting algorithms, using automated bots and leveraging advanced arbitrage techniques like surebetting and value betting to secure guaranteed profits. These activities often fall under the radar but can lead to significant financial losses for betting platforms and honest bettors.
What is Surebet?
Surebets, also known as arbitrage bets or “arbs,” are a betting strategy that involves placing bets on all possible outcomes of an event across different bookmakers to guarantee a profit, regardless of the result. This strategy takes advantage of differing odds offered by various bookmakers. The key idea is to find a set of odds that, when used to place proportional bets, will result in a profit no matter which outcome occurs.
How Surebetting impacts the market?
Surebetting leads to payout losses for bookmakers, as bettors capitalize on odds discrepancies across platforms to secure guaranteed profits. This practice disrupts the typical risk structure, reducing bookmakers’ expected profits and increasing operational costs to manage and limit arbitrage activity.
Impact of surebets on the iGaming industry
Surebets have a complex and multifaceted impact on the iGaming industry, presenting both challenges and opportunities.
Positive impacts
- Increased competition: The presence of surebets encourages bookmakers to offer more competitive odds, which can benefit bettors by providing better value.
- Market efficiency: Surebets can help to correct inefficiencies in the betting market by quickly exploiting discrepancies in odds. This can lead to more accurate odds and a more balanced betting environment. Research on European football has shown a correlation between the rise of online betting platforms and an increase in surebet opportunities, leading to a decrease in bookmaker margins.
- Economic growth: In some regions, the introduction of surebet platforms has been linked to economic growth. For example, Transatlantic Capital’s acquisition of the SUREBET platform in Kenya is expected to drive economic growth in the East African market.
Negative impacts
While surebets offer certain benefits, they also present challenges for the iGaming industry.
- Reduced bookmaker profits: Surebets can negatively impact bookmaker profits by guaranteeing profits for bettors, essentially eliminating the bookmaker’s margin. Furthermore, factors like “corridors” and “lack of luck” can further affect the efficiency of various betting strategies, including surebets, adding to the complexity of managing risk for bookmakers.
- Increased risk of fraud: Surebets can be exploited by fraudsters using various methods, such as creating multiple accounts, using stolen identities, or employing bots to automate betting. Bookmakers also face risks related to “palpable errors” in odds and the potential for bet cancellations, which can lead to financial losses.
- Erosion of trust: Surebet fraud can erode trust in the fairness and integrity of the iGaming industry, potentially leading to a decline in player participation.
Financial losses due to surebetting
While precise figures on losses incurred by the iGaming industry, specifically due to surebetting, are not readily available, it’s essential to consider the broader context of fraud in the industry. A study by the American Gaming Association estimated that Americans wagered approximately $337.9 billion with illegal iGaming websites in 2023, resulting in a loss of $3.9 billion in state tax revenue. These figures underscore the substantial financial impact of fraudulent activities, including potential losses.
Recent cases of surebet fraud
Recent news articles highlight the ongoing issue of surebet fraud. In December 2024, Cory Zeidman, a professional poker player, pleaded guilty to federal wire fraud charges related to a sports betting scam that defrauded people out of millions of dollars. Zeidman and his group falsely claimed to have insider information that could guarantee winning bets, misleading numerous victims. Law enforcement agencies are actively investigating and prosecuting individuals involved in such schemes, as demonstrated by the case against Zeidman, who now faces up to 20 years in prison and significant financial penalties. This case highlights the need for continued vigilance and robust fraud prevention measures within the iGaming industry.
Legality and ethical considerations
The legality of surebets varies depending on the jurisdiction. In most cases, surebetting itself is not illegal. However, it’s crucial for bettors to verify that online sports betting is legal in their jurisdiction and to be aware that bookmakers may have terms and conditions that prohibit or restrict the practice, potentially leading to penalties.
Ethically, surebets raise concerns about fairness and the potential for exploitation. While some argue that it is a legitimate strategy that takes advantage of market inefficiencies, others view it as a form of advantage play that undermines the integrity of sports betting. The ethical implications of sports betting extend beyond surebets, encompassing concerns about the potential for harm to vulnerable individuals, the need for social safeguards, and the targeting of college athletes.
Surebet calculator
- Finding the surebet: The first step is identifying an event where different bookmakers offer sufficiently varied odds. This variation allows fraudsters to cover all possible outcomes. For instance, if one bookmaker offers odds on a tennis match for Player A to win while another offers higher odds on Player B to win, a surebet opportunity may exist.
- Calculating the stake: Once a surebet opportunity is identified, the next step is calculating the stakes. The fraudster must bet an amount on each outcome in proportion to the odds, ensuring that the total payout will be greater than the total amount staked, regardless of the outcome.
- Placing the bets: After calculating the required stakes, the fraudster places the bets across different bookmakers. This must be done quickly to avoid changing odds, which could eliminate the arbitrage opportunity.
To crystalize this concept further, imagine a tennis match between Player A and Player B, with two different bookmakers offering the following odds:
|
Bookmaker 1 |
Bookmaker 2 |
|||
| Player A | 2.10 | 1.85 | ||
| Player B | 1.90 | 2.05 | ||
In this scenario, the odds offered by bookmaker 1 for Player A to win is 2.10, and 1.90 for Player B to win, whereas another bookmaker offers the odds of 1.85 for Player A to win and 2.05 for Player B to win. Fraudsters can exploit this variation by placing the following bets:
- Bet $100 on Player A to win at Bookmaker 1 (odds of 2.10).
- Bet $95.24 on Player B to win at Bookmaker 2 (odds of 2.05).
Regardless of who wins, the return would be:
- If Player A wins: $100 x 2.10 = $210 (profit: $210 – $100 – $95.24 = $14.76)
- If Player B wins: $95.24 x 2.05 = $195.24 (profit: $195.24 – $95.24 – $100 = $14.76)
In this way, the fraudster secures a guaranteed profit of $14.76, irrespective of the match outcome.
How are surebets scaled and automated?
Scaling the surebetting process using dedicated software or web services that involves leveraging technology to efficiently manage a high volume of bets across multiple bookmakers and events. The key to successful scaling is automating and optimizing various aspects of the surebetting process, allowing fraudsters to increase their betting volume while maintaining accuracy and minimizing risk.
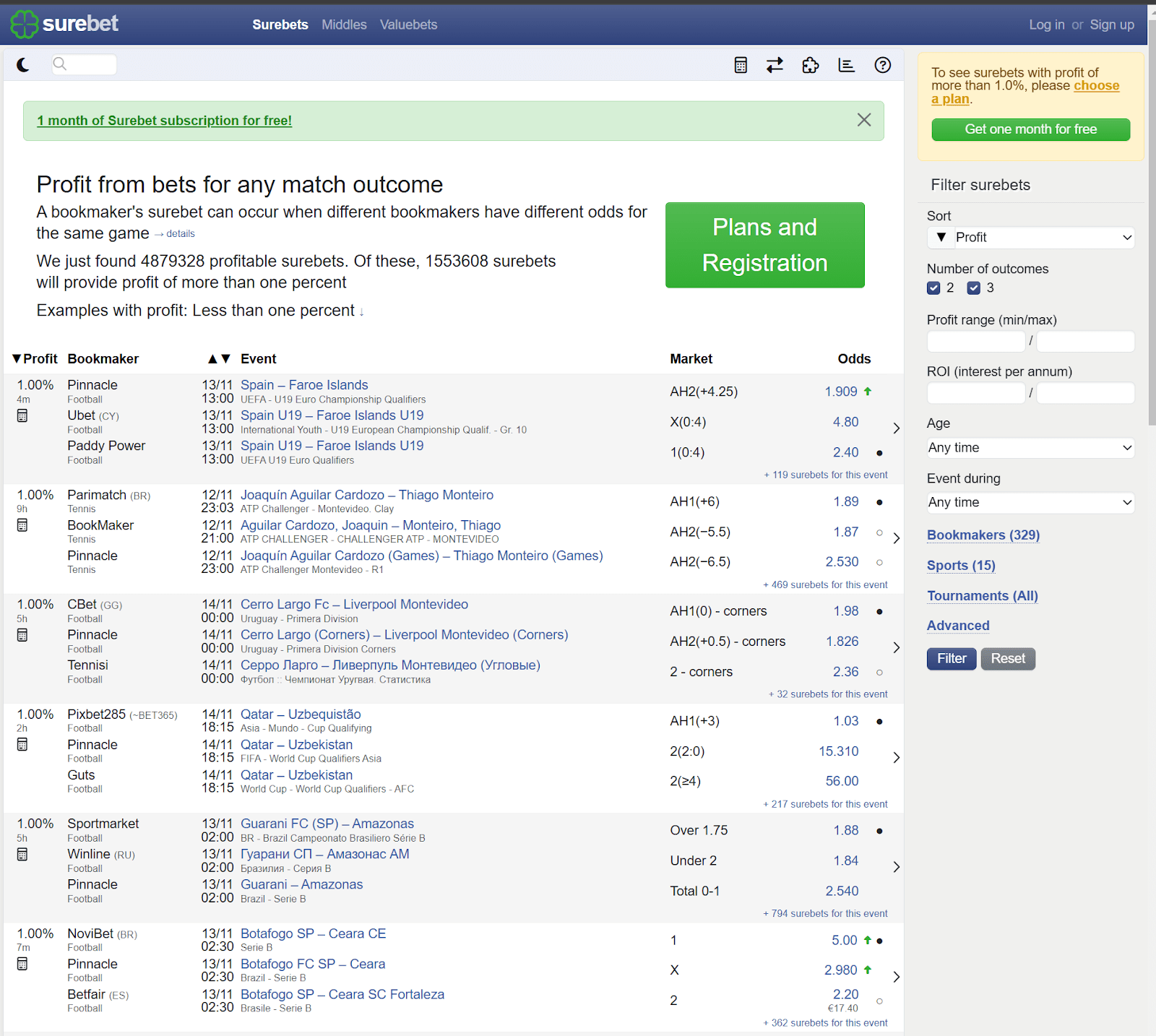
Figure 1. A screenshot of a surebet service dashboard
Here are some insights into how this scaling can be achieved:
- Multiple accounts: Creating multiple accounts with different bookmakers to circumvent betting limits and maximize surebet opportunities.
- Identity theft: Using stolen or fake identities to create accounts and bypass Know Your Customer (KYC) checks.
- Bonus abuse: Exploiting bonus offers and promotions by creating multiple accounts to claim bonuses repeatedly.
- Automated bots: Employing bots to automate the process of finding and placing surebets, allowing fraudsters to exploit opportunities faster and more efficiently. These bots can significantly negatively impact iGaming operators, draining advertising budgets and reducing conversion rates by generating fake clicks and engagement. Furthermore, bots can create an unfair playing field in online gaming services, leading to player complaints and damage to the operator’s reputation.
- Collusion: Collaborating with other fraudsters to manipulate odds or create artificial surebet opportunities.
- Data aggregation: Surebetting services collect and provide odds data from multiple bookmakers, streamlining the data collection process. Using such services, bettors can access vast odds data without scraping each bookmaker’s website. This aggregation simplifies scaling by providing a single access point for odds data.
- Integration with betting platforms: Surebetting services can integrate with various betting platforms and exchanges, enabling seamless bet placement. This integration allows for quicker execution of bets and reduces the chances of errors, which is essential when scaling up the betting volume.
- Real-time odds monitoring: Automated software can monitor the odds across hundreds of bookmakers simultaneously, 24/7. This real-time monitoring ensures that surebet opportunities are identified immediately as they arise. The software collects odds data and compares them using advanced algorithms, significantly increasing the speed and accuracy of identifying surebets.
- Algorithmic analysis: Advanced surebetting software uses algorithms to analyze the odds data, calculate potential profits, and assess the risk associated with each surebet opportunity. This process allows for quick decision-making, ensuring the user can act on profitable opportunities before the odds change.
- Centralized muti-account management and control: Surebetting software can manage multiple betting accounts across bookmakers from a single interface. This centralized control simplifies account management and allows users to place bets on multiple accounts simultaneously, reducing the time and effort required to manage each account individually.
Figure 2. Account Management Dashboard across different bookies
- Automated login and bet placement: To efficiently manage multiple accounts, the software can automate the login process and simultaneously place bets across different accounts. This automation is crucial for scaling the betting process, as it enables users to handle many bets without manual intervention.
- Betting process execution: Betting bots can automatically execute bets based on pre-defined rules and strategies. These bots can place bets on identified surebet opportunities with precision and speed, which is critical for scaling as it minimizes the risk of missing out on profitable bets due to delays.
- Adaptability: Advanced betting bots can adapt to changing market conditions. For example, if odds change before all bets are placed, the bot can re-calculate the optimal stakes or adjust the betting strategy accordingly. This adaptability ensures that the scaling process does not compromise the profitability or security of the bets.
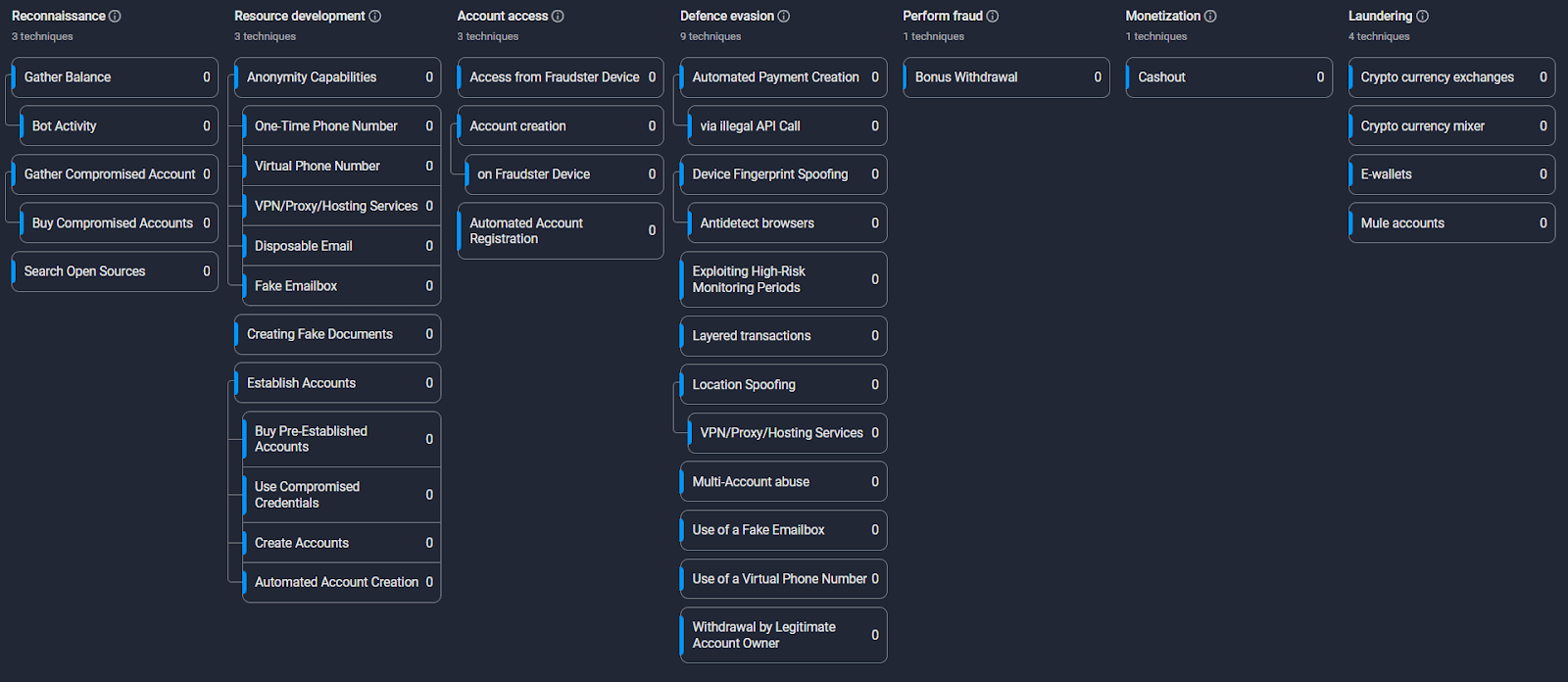
Surebet fraud scheme participants
- Fraudster
The fraudster, the mastermind behind the entire operation, is responsible for orchestrating the scheme. They set up the necessary infrastructure, including creating accounts and controlling the betting bot. The fraudster aims to exploit odds discrepancies for guaranteed profit and then launder the winnings through cryptocurrency platforms. - Betting bot
This is an automated tool controlled by the fraudster. The betting bot is programmed to monitor surebetting opportunities in real-time, place bets across multiple bookmakers, and handle the entire betting process autonomously. Its role is crucial for executing bets swiftly, ensuring that profitable opportunities are not missed due to delays in manual operations. - Surebetting service
A specialized service that aggregates and analyzes real-time odds from various bookmakers. It is designed to detect surebets—situations where betting on all possible outcomes of an event guarantees a profit. The surebetting service constantly scans for odds discrepancies and feeds this information to the betting bot, enabling automated betting. - Betting accounts
These are the accounts opened by the fraudster with various bookmakers. Each account is used to place bets across different platforms. By using multiple accounts, the fraudster can spread their activity and avoid drawing too much attention to any single account. - Bookmakers
The online platforms that provide odds and accept bets on various events. Bookmakers set odds based on their own assessment of the likelihood of outcomes. These odds can vary between platforms, creating arbitrage opportunities that the fraudster exploits. Bookmakers also process bets and distribute winnings after events conclude. - Mule accounts
Secondary betting, bank, or e-wallet accounts that the fraudster sets up under false identities or recruits from third parties. These accounts are used to withdraw, deposit, and transfer funds in a way that makes the fraudster’s network look legitimate and difficult to trace. By using mule accounts, the fraudster can create multiple layers of transactions that shield their real identity and make law enforcement’s job much more difficult. - E-wallets
Digital payment systems like Skrill, Neteller, and PayPal act as intermediaries for the fraudster’s funds. E-wallets are often linked to the primary and mule accounts, serving as a buffer that further anonymizes the movement of funds. They allow quick, low-profile transfers between accounts and can be connected to cryptocurrency platforms, making them a preferred tool for laundering the winnings into untraceable digital assets. - CryptoPlatforms
Cryptocurrency exchanges or services where the fraudster converts their betting profits into cryptocurrency. These platforms are used to launder the funds, providing anonymity and making it difficult for authorities to trace the money’s origins. The fraudster may also use cryptocurrency mixing services to further obscure the transaction history before withdrawing funds.
Fraudulent scheme execution
Establish betting accounts
The fraudster creates multiple betting accounts at different bookmakers, often using fake or stolen identities to avoid detection. These accounts are essential for placing bets across various platforms, allowing the fraudster to exploit odds discrepancies. By diversifying accounts, the fraudster reduces the risk of being flagged by any bookmaker.
Mitigation & controls
- KYC (Know Your Customer) verification
KYC procedures’ purpose is to verify the identity of users before they can open accounts or place bets. This includes, but is not limited to:- Document checks: Requiring users to submit government-issued IDs, utility bills, and other documents that prove identity and address.
- Biometric verification: Incorporating facial recognition and fingerprint scanning ensures the person opening the account is the genuine owner of the submitted documents.
- Enhanced due diligence: Conduct additional checks for high-risk users, such as those using proxies, VPNs, or fake information.
- Device fingerprinting
Device fingerprinting technology can detect patterns in device usage across multiple accounts. This involves identifying unique characteristics of a user’s device (e.g., IP address, browser configuration, device type) and flagging accounts that share the same or similar device fingerprints. This can prevent fraudsters from using the same device to create multiple betting accounts under different identities.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for logging into accounts ensures that access is not solely based on a username and password but also requires an additional verification method, such as a one-time code sent to a mobile device or email.
- Account activity monitoring
Monitoring account activity helps identify unusual patterns that suggest fraudulent behavior, especially during registration. This includes, but is not limited to:- Registration velocity;
- Network anonymization controls;
- Anti-detect browsers identification
Odds data collection and surebets calculation
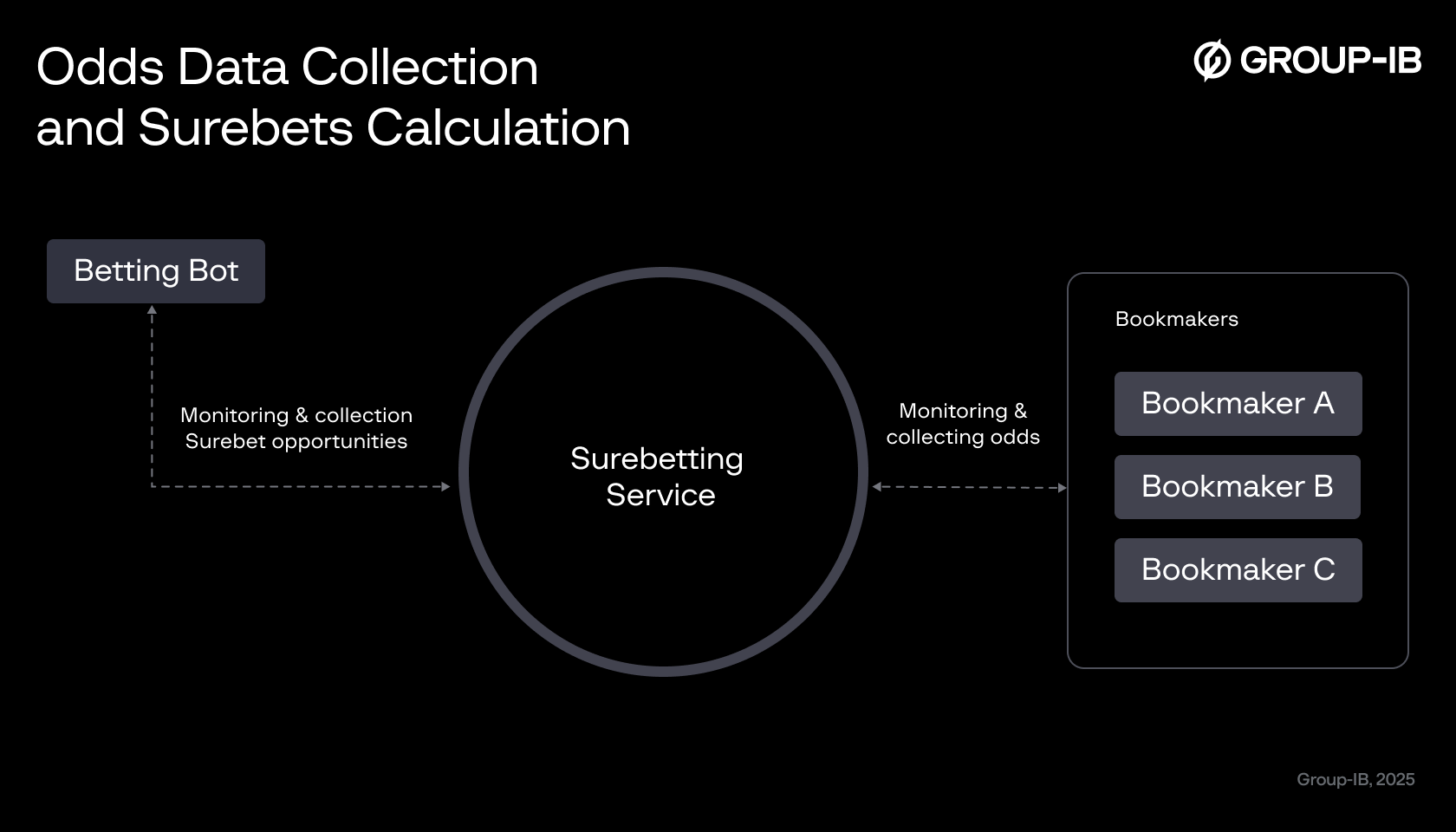
Figure 3. Odds Data Collection and Surebets Calculation
Collecting odds data
A surebetting service scans and collects odds from multiple bookmakers. This data is fed into algorithms designed to detect discrepancies where betting on all outcomes ensures a guaranteed profit (known as surebets). These odds fluctuations, which occur because different bookmakers have varying opinions on the likelihood of outcomes, are what the fraudster relies on.
Monitoring surebet opportunities
The betting bot is programmed to monitor odds in real-time by connecting to the surebetting service. The bot identifies when and where arbitrage opportunities emerge as odds fluctuate rapidly, enabling the fraudster to act fast. This automated process ensures that every profitable opportunity is noticed, even for fleeting moments when the odds align perfectly.
Mitigation & controls
- Real-time monitoring of odds data access
Bookmakers should implement real-time monitoring systems to detect automated and abnormal access patterns. They can identify potential abuse by closely monitoring API or web traffic, such as bots scraping odds data at high speeds or unusual frequencies. This ensures that the collection of odds data is limited to legitimate users and is not being exploited by surebetting services. - Rate limiting on odds data requests
Implementing rate limiting can restrict the number of times an IP address or user account can request odds data within a specific timeframe. This prevents bots from continuously scraping large amounts of data from multiple bookmakers and using it for surebetting purposes. Rate limiting can significantly reduce the efficiency of automated odds collection tools used by fraudsters. - Bot protection technologies
Bot Protection technologies can be integrated into websites and APIs to block automated scraping of odds data. Fraudsters often rely on bots to collect odds at high frequencies and compare them for arbitrage opportunities. Behavioral Analysis, in combinations with bot protection technologies, can prevent bots from gaining access to odds data. - Anomaly detection algorithms for surebetting patterns
Using machine learning models, bookmakers can detect patterns in user activity that suggest odds data is being collected for surebetting purposes. For example, users or bots that request odds from a broad range of events or sports or repeatedly compare odds from different bookmakers could trigger fraud alerts. These algorithms can spot anomalies in data access and betting patterns, allowing bookmakers to act quickly.
Betting process automation
Once the surebet opportunities are identified, the fraudster instructs the betting bot to begin the betting process. The bot automatically places bets across multiple bookmaker accounts, covering all potential event outcomes. This ensures that the fraudster will win regardless of the result, effectively gaming the system.
The betting bot fully controls the operation by logging into various betting accounts and confirming available balances. It places simultaneous bets across different bookmakers, ensuring that all possible sporting event outcomes are covered. After the event, the bookmakers process the bets and credit the winnings to the fraudster’s accounts that bet on the winning outcome.
Mitigation & controls
- Behavioral analysis of betting patterns
Implementing behavioral analysis systems can help bookmakers detect patterns that indicate the use of automated betting bots. Typical signs include placing bets at consistent intervals, betting across multiple bookmakers at once, or placing identical bets on the same event within seconds. Bookmakers can identify and flag accounts exhibiting unusual or automated behavior by monitoring these patterns. - Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Requiring multi-factor authentication for account logins and large transactions can disrupt bots from gaining easy access to betting accounts. Suppose bots are programmed to place automated bets. In that case, they will be blocked at the point of MFA verification, as they cannot respond to an authentication prompt sent to a legitimate user’s mobile device or email. - IP and device fingerprinting
IP tracking and device fingerprinting technologies help detect when the same device or IP address is being used to place bets across multiple accounts. Bots often operate through centralized networks or cloud infrastructure, making it easier to flag suspicious betting activity originating from the same devices or networks. Suspected accounts can be suspended for further verification. - Imposing bet limits and cooldown periods
Bookmakers can set bet limits for high-risk accounts or impose cooldown periods between bets to disrupt the rapid-fire betting patterns typical of bots. For example, restricting the number of bets a user can place in a given timeframe, or adding a small delay between each bet, can limit the ability of bots to place multiple bets across all possible outcomes in a surebet scenario. - Rate limiting on account actions
Implementing rate limiting on account actions, such as logging in, placing bets, or performing balance checks, can slow down bots. Fraudulent bots typically perform these actions in rapid succession, and rate limiting ensures that any bot activity is throttled, making the process inefficient and reducing the likelihood of successful arbitrage betting. - Transactional anomaly detection
Anomaly detection algorithms can be employed to detect transactional anomalies related to betting activities. For example, frequent betting on all possible outcomes of the same event across different accounts, or unusual betting volumes across similar events, can be red flags for fraud. Anomaly detection systems can automatically flag suspicious transactions for manual review.
Funds withdrawal & laundering
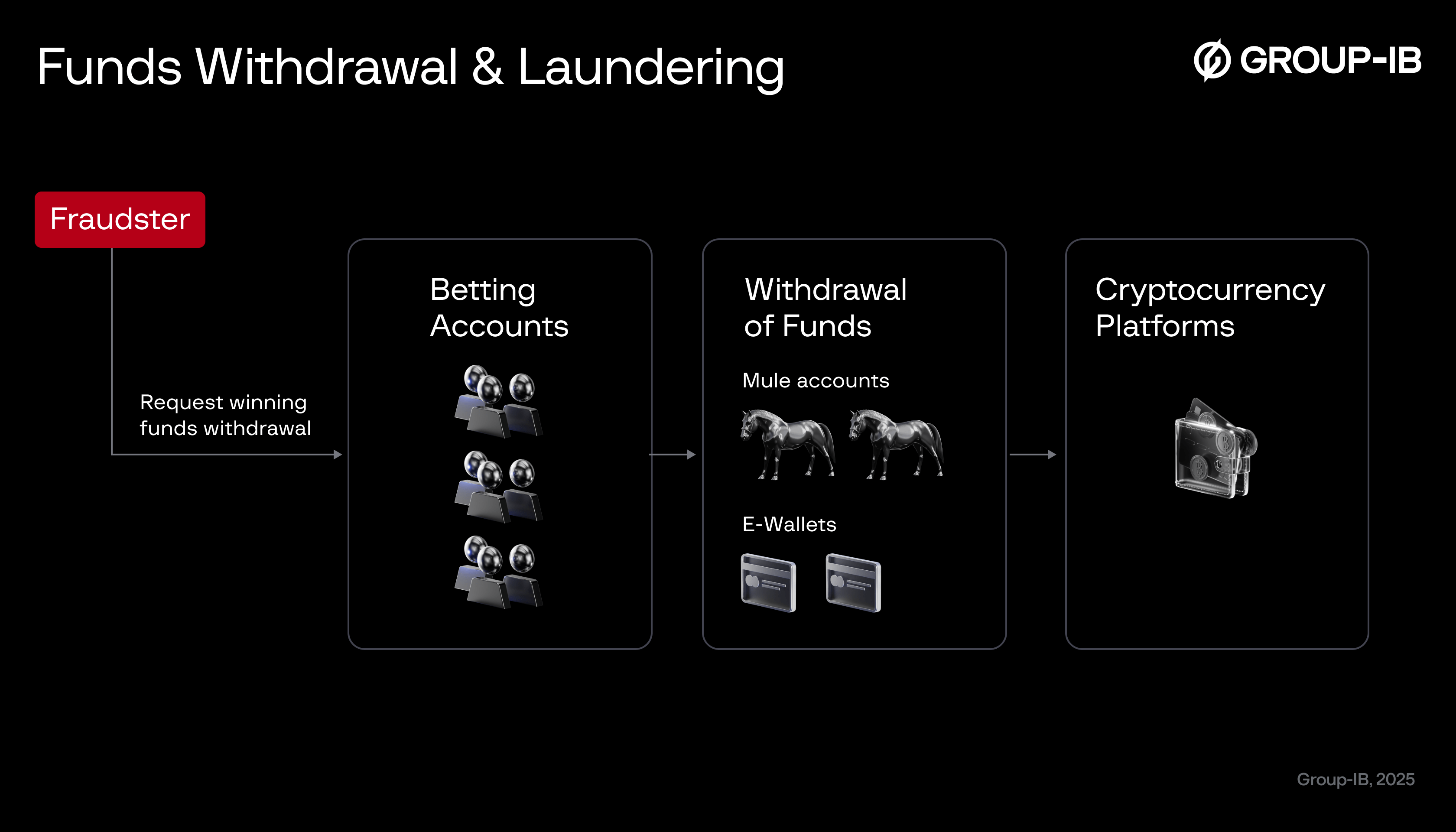
Figure 4. How funds are withdrawn and laundered
Request fund withdrawals
After generating winnings from the arbitrage scheme, the fraudster initiates withdrawals from the bookmaker accounts, often using a network of mule accounts under different identities. This disperses the withdrawals to various bank accounts or e-wallets like Skrill, Neteller, or PayPal. By leveraging these channels, the fraudster minimizes the chances of triggering anti-fraud alerts and creates multiple layers of transactions, making it more challenging for authorities to trace the funds back to a single source.
Mitigation & controls
- Enhanced KYC and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) protocols
Enforced rigorous KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML procedures for withdrawals implemented by bookmakers and financial institutions, includes but is not limited to:- Increased verification for withdrawals to newly added bank accounts or e-wallets.
- Cross-checking withdrawal requests against AML watchlists and suspicious activity patterns.
- Continuous monitoring of user accounts flagged for prior suspicious behavior or frequent small withdrawals to multiple accounts.
- Real-time transaction monitoring
Implementing real-time transaction monitoring systems can help identify unusual withdrawal patterns that indicate fraud or money laundering. These systems can flag:- Frequent, low-value withdrawals to multiple bank accounts or e-wallets (a hallmark of using mule accounts).
- Withdrawals spread across multiple geographies or financial platforms within a short period of time.
- Uncharacteristic behavior, such as a sudden increase in withdrawal frequency or value compared to past account activity.
- Limits on withdrawals to multiple accounts
Bookmakers can impose restrictions on how and where funds can be withdrawn by:- Limiting the number of linked accounts (bank accounts or e-wallets) that a single user can withdraw funds to.
- Setting thresholds for maximum daily or weekly withdrawal limits, especially for newly created or unverified accounts.
- Requiring additional verification steps for users who attempt to withdraw to new accounts or platforms like Skrill, Neteller, or PayPal.
- Detection of layered withdrawals
Utilize machine learning algorithms to detect patterns of layered withdrawals, where fraudsters break large sums into smaller transactions to evade detection. Key indicators include:- Multiple small withdrawals timed close together but under-reporting thresholds.
- Withdrawal requests directed toward accounts linked to known mule activities or flagged as suspicious in past transactions.
- Monitoring of mule accounts and e-wallet activities
E-wallets (like Skrill, Neteller, or PayPal) and mule accounts used for laundering can be flagged through the use of:- Device fingerprinting: Tracking devices and IP addresses linked to multiple accounts across different users, detecting mules who facilitate the same withdrawal channels.
- Monitoring accounts that receive frequent incoming transactions from betting sites but exhibit limited spending or transaction activity beyond withdrawal.
- Cross-referencing with blacklisted or flagged accounts in collaboration with other platforms to identify mule networks.
- Multi-layered verification for high-risk withdrawals
For higher-risk withdrawals, implement multi-layered verification protocols that involve:- Requiring multi-factor authentication (MFA) for every large withdrawal or withdrawal to new accounts.
- Requiring additional forms of identification or manual review for withdrawals to high-risk e-wallets or to multiple new accounts.
- Imposing cooldown periods for large or unusual withdrawal requests, giving the system time to detect patterns before funds are fully dispersed.
- Withdrawal delay and review mechanisms
Implementing delayed processing for large or complex withdrawal requests provides additional time to assess risk. During the delay:- Withdrawal requests can be flagged for manual review if they exceed certain thresholds or exhibit unusual patterns.
- Automated systems can cross-check data across multiple platforms for known mule accounts or suspicious behavior, providing time to prevent fraudulent withdrawals.
Convert funds to cryptocurrency
The fraudster transfers the dispersed funds into cryptocurrency exchanges from the mule accounts or linked e-wallets. Once converted into digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum, the funds are run through mixing services. These services blend transactions from multiple sources, effectively “laundering” the funds by severing the link between the sender and the recipient. The fraudster may also move the money between different cryptocurrencies and wallets, creating a complex web of transactions that conceals the money trail.
Request cryptocurrency withdrawal
Once the funds have been sufficiently anonymized through layering, the fraudster withdraws the cryptocurrency into a private digital wallet. From there, the laundered assets can either be used directly for purchases or converted back into fiat currency through third-party services, peer-to-peer exchanges, or even reintroduced into traditional financial systems through e-wallets or mule accounts. At this point, the fraudster has successfully laundered the betting profits, making them appear legitimate and free of suspicious origins.
Modus Operandi
Conclusion
Arbitrage betting fraud represents a highly organized and technologically advanced form of betting fraud. By leveraging automation, anonymity tools, and sophisticated techniques for account creation and defense evasion, fraudsters can exploit betting platforms’ weaknesses to generate consistent profits.
Key risk indicators
- Transition to the bookmaker’s site from a well-known surebetting/arbitrage service: Traffic originating from these sites is a red flag for automated or coordinated betting, as users leveraging such tools are more likely engaging in arbitrage. This can indicate organized betting behavior designed to exploit odds gaps.
- Use of disposable emails and virtual phone numbers for account creation: Disposable emails and virtual numbers provide anonymity and are often used by bettors looking to create multiple accounts, avoid detection, and evade penalties imposed by bookmakers on previously flagged accounts.
- Presence of automation tools during account authorization and bet placement: The use of automation tools, such as betting bots or browser extensions, enables rapid bet placement on odds that quickly shift, creating an advantage for arbitrage bettors. This automation circumvents manual actions, allowing surebettors to place high-frequency bets that aren’t easily detected by traditional monitoring systems.
- Multiple accounts linked to the same device, device fingerprint, or IP address: Device and IP duplication across accounts can indicate multi-accounting, a strategy where surebettors use multiple accounts to increase betting limits, leverage promotions, and reduce detection. Bookmakers often look for patterns in device usage to detect such linked accounts.
- Multiple bonus requests: Surebettors often target bonuses or promotional offers, using them to improve profit margins. High-frequency or suspicious bonus requests from a single account or multiple linked accounts can indicate bonus abuse, a tactic common among arbitrage bettors.
- Presence of a surebetting browser extension: The presence of browser extensions dedicated to surebetting or odds comparison provides direct evidence of arbitrage intent, as these extensions streamline the process of finding and exploiting favorable odds.
- Unusual betting patterns or timing: Arbitrage bettors often place bets close to real-time odds changes to secure the most favorable conditions. Frequent bets made within seconds of odds adjustments or near event start times can signal surebetting activity.
- Consistent small profits across multiple events: Surebettors aim for small but guaranteed profits on each event, leading to a pattern of low-risk, low-reward bets across various outcomes. This type of betting behavior can differ from traditional bettors, who typically have more varied winnings and losses.
- Frequent withdrawals and low average bet duration: Bettors using surebetting techniques may cash out frequently, as their goal is to secure immediate profits rather than wait for high stakes to settle. This behavior, combined with quick bets, can signal an arbitrage-focused account.
Recommendations
To cope with surebettors there are next actions bookmakers need to consider:
- Implement real-time monitoring of betting flows to detect atypical betting patterns promptly.
- Conduct user profiling based on betting behavior to identify patterns consistent with arbitrage activity.
- Activate automated responses upon detection of irregularities, including setting betting limits or adjusting odds dynamically.
- Identify and track betting networks or user groups exhibiting coordinated behaviors indicative of arbitrage.
- Perform risk-based analysis of referral sources to detect high-risk origins and assess potential patterns in user acquisition.