Digital footprints are ubiquitous, and the distinction between publicly available information and private intelligence is often blurred. A massive amount of data exists, from social media profiles to online forums. Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) sits at the intersection of visibility and vulnerability.
It involves collecting information from publicly available sources. It is used by cybersecurity professionals, law enforcement, and even cybercriminals to gather insights, track targets, or plan attacks.
The term OSINT originated from the military, referring to the gathering of intelligence from open sources rather than secret channels. That definition still holds, but now open sources include Google search results, private forum posts, or metadata hidden in social media photos.
While more challenging to find, content behind logins or paywalls is still considered public if it’s not protected by law.
In cybersecurity, OSINT has evolved into both a defensive asset and an offensive tool. This article examines how open source intelligence is gathered, its significance, and its application by both protectors and predators.
What is Open Source Intelligence (OSINT)?
OSINT refers to the process of collecting and analyzing publicly accessible data to uncover potential threats and security risks. This includes monitoring social media activity, breach dumps, public code repositories, news coverage, and government records. Although the sources are unclassified, the intelligence derived from them can be highly valuable when interpreted in context.
For example, security analysts may identify a newly registered domain that closely resembles a known brand’s website. Paired with discussions on underground forums about phishing campaigns, this insight can help security teams flag the domain, notify the brand, and block associated activity before users fall victim.
OSINT is critical in enabling proactive defense by turning publicly available information into early warnings that support faster and more effective responses.
Importance of OSINT in Cybersecurity
In 2023, Future Market Insights projected that the OSINT market will reach $58.21 billion by 2033. This growth reflects a fundamental change in how cybersecurity teams approach threat detection. With so much information now publicly available, attackers can easily uncover exposed assets, leaked credentials, or infrastructure details without breaching a single system.
The same public data that empowers attackers can also be leveraged by defenders. When monitored strategically, it becomes a rich source of early warning signals. Security teams can track threat actors, identify suspicious domain registrations, and detect chatter about vulnerabilities long before traditional tools would raise an alert.
The reason traditional security tools fall short is because they often operate within the network perimeter. They detect threats after damage is already underway. OSINT fills that gap by offering visibility into external risks in real time, helping you stay ahead of potential breaches instead of reacting to them.
- Early Threat Detection: Monitoring public sources allows security teams to spot early signs of cyberattacks. With Group-IB’s Threat Intelligence platform, you can uncover vulnerabilities in your infrastructure and detect threats before they become incidents.
- Risk Mapping: Open source intelligence provides a broader view of the cyber threat landscape, complementing internal data with external insights.
- Economically Viable: The OSINT framework provides in-depth insights into probable and potential threats, offering a cost-effective method for discovering critical information.
- Support for Incident Response: After a security breach, OSINT helps gather critical details for swift and effective incident response.
OSINT Framework and Its Applications
The sheer volume of data and information publicly available is sufficient to overwhelm even the most experienced cybersecurity experts. An OSINT framework provides a structured method to conduct open-source intelligence research. It enables organizations to identify and extract key data points and information. The process involves the following steps:
- Collection: Gathering data from public domains, including social media, forums, blogs, and news sites.
- Processing: Converting raw data into a format suitable for analysis.
- Analysis: Using OSINT techniques and expert observation to identify patterns, trends, and potential security risks.
- Dissemination: Sharing findings with relevant stakeholders to enable timely defensive actions.
The OSINT framework offers a structured way to make sense of the vast, unstructured data scattered across the internet. In cybersecurity, it helps transform publicly available information into timely, actionable insights. When used effectively, OSINT becomes a powerful tool for:
- Detecting emerging cyber threats and attack patterns
- Mapping digital footprints of individuals, organizations, or threat groups
- Identifying exposed infrastructure, misconfigured services, or leaked credentials
- Monitoring forums, social platforms, and code repositories for risk signals
- Tracking stolen data and mentions on dark web markets
- Verifying identities, affiliations, and suspicious domain registrations
- Analyzing metadata from leaked documents and images
- Pinpointing locations using geotags and digital breadcrumbs
- Spotting coordinated misinformation campaigns or bot activity
These capabilities enable you to anticipate threats, close gaps before they’re exploited, and take control of your security posture long before an incident occurs.
At Group-IB, OSINT is a core component of our Threat Intelligence solution, which integrates open-source signals with deep technical and dark web intelligence. This enables your security team to prioritize threats, uncover targeted campaigns, and make faster, more informed decisions.
Common OSINT Techniques for Data Collection
Common OSINT techniques used in cybersecurity help professionals uncover critical information, validate sources, and build a clearer picture of potential threats. Some of the most widely used methods include:
- Social Media Monitoring: Analyzing user posts and interactions on platforms like Twitter, LinkedIn, and Facebook for potential threats.
- Google Dorks: Many companies today publish millions of pages, making it difficult to track them all. Sometimes, organizations and even threat actors miss the traces they leave behind on the internet. Google Dorking is a technique that involves crafting queries to find hidden or unindexed pages on Google, allowing access to confidential information that can aid in both preventing and conducting cyber attacks.
- Dark Web Monitoring: Threat actors frequently use prominent forums on the dark web to promote their activities. Meticulously tracing conversations and identifying patterns through dark web monitoring can help gain crucial information.
- Domain and IP Analysis: Investigating domain registration data and IP addresses enables you to identify malicious actors and their activities.
- Metadata Extraction: Analyzing metadata from images, documents, and files to gain insights into data origin and modifications.
- Geolocation Techniques: Determining the physical locations of servers, websites, or individuals through public records.These techniques enhance OSINT cybersecurity efforts by helping teams connect the dots across disparate data sources. When analysts can quickly validate signals and identify patterns in real time, investigation fatigue is reduced, and they can more confidently focus on high-impact threat
OSINT Tools and Resources for Investigators
OSINT research relies on specialized tools to efficiently collect and analyze publicly available data. These tools improve the speed of investigations, reduce human error, and provide deeper visibility into potential threats. Commonly used online OSINT tools include:
Digital Risk Protection by Group-IB
Group-IB’s Digital Risk Protection enhances OSINT cybersecurity by actively monitoring digital risks across the Internet, including brand abuse, data leaks, and the exposure of sensitive information.
At the core of this solution is our in-house Network Graph Analysis Tool, designed to uncover and dismantle threat actor infrastructure. This approach is particularly effective for tracking online vulnerabilities and managing your external risk profile, critical for defending against today’s fast-evolving cyber threats.
Maltego
Maltego is a powerful OSINT tool developed by Paterva, renowned for its ability to perform detailed digital reconnaissance. It utilizes “transforms” to integrate and analyze data from external applications, allowing users to map complex relationships between entities such as IP addresses, domains, and organizations.
Maltego offers both free and commercial versions, catering to different investigative needs. It is a powerful tool for visualizing relationships between pieces of information.
Shodan
Dubbed the “search engine for the Internet of Things (IoT),” Shodan allows users to discover devices connected to the Internet. It indexes information about various devices, including servers, routers, and webcams, providing insights into their configurations and potential vulnerabilities.
theHarvester
theHarvester is an essential tool for gathering emails, subdomains, hostnames, open ports, and more from public sources. It collects data from various platforms, including search engines like Google and Bing, and social networks like LinkedIn. This tool is particularly useful in the initial stages of penetration testing.
SpiderFoot
SpiderFoot automates the process of gathering OSINT from over 100 public data sources. It assists in mapping a target’s digital footprint, including information on IP addresses, domain names, email addresses, and other relevant details. SpiderFoot is designed to be both scalable and customizable, making it suitable for various investigative needs.
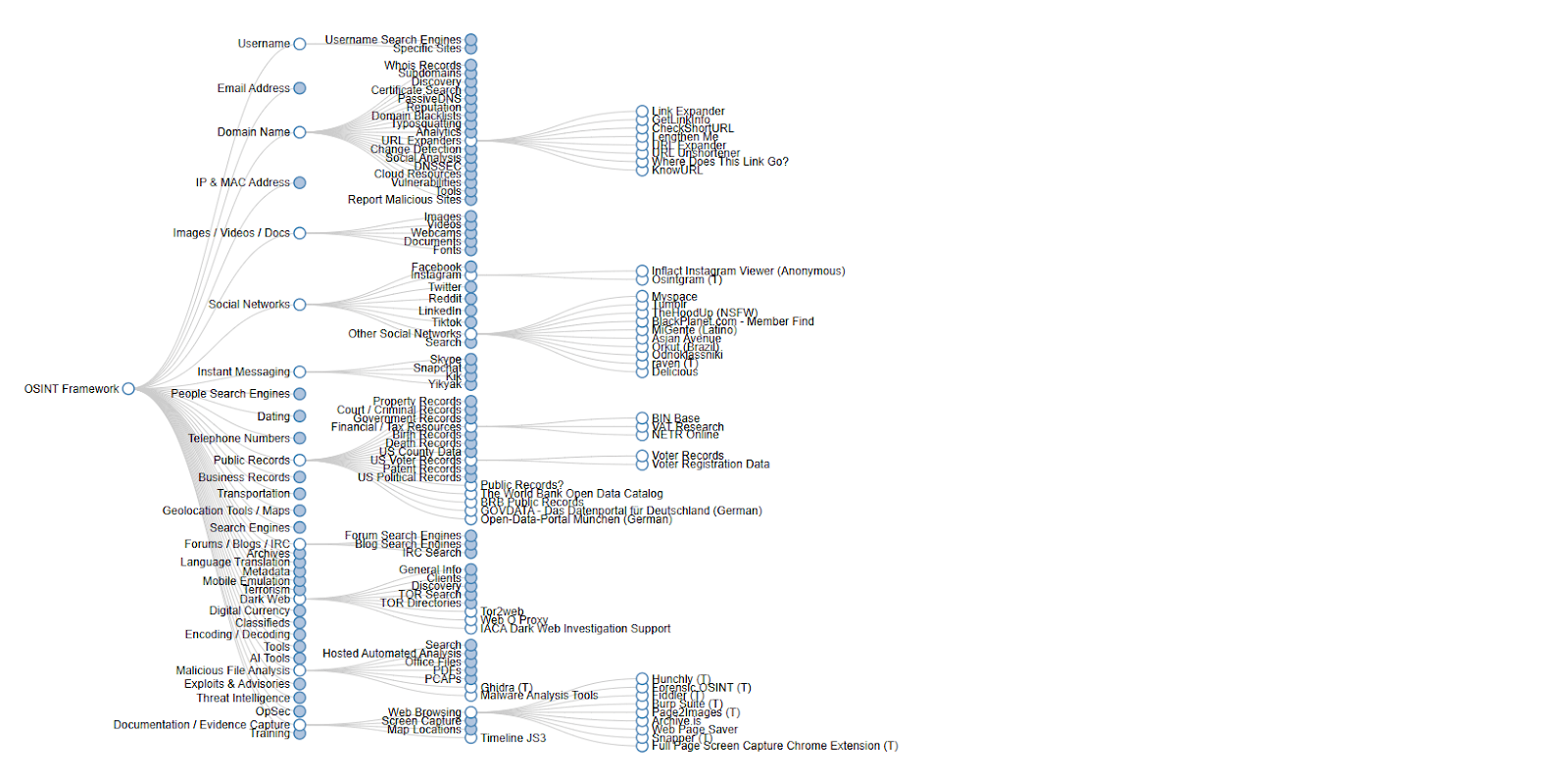
OSINT Framework
The OSINT Framework is a web-based resource that organizes a multitude of OSINT tools and resources by category. It serves as a valuable starting point for investigators looking to explore various data sources and tools available for open source intelligence gathering.
Each tool has its strengths and can be used in conjunction with one another to provide a comprehensive view of the threat landscape.
How OSINT is Used in Cybersecurity Threat Detection
Integrating OSINT into threat detection processes has revolutionized modern cybersecurity. Continuously scanning sources for emerging risks enables:
- Proactive Identification of Vulnerabilities: Early warnings allow for the remediation of weaknesses before they are exploited.
- Enhanced Incident Response: Real-time intelligence from open source intelligence streamlines the decision-making process during security incidents.
- Threat Actor Profiling: Gathering detailed information about threat actors helps understand their tactics, techniques, and procedures.
- Market and Competitor Analysis: Beyond security, OSINT cybersecurity insights can inform business strategies and market positioning.
At Group-IB, we expand this capability through our Threat Intelligence platform. It correlates data from across the dark web, social media, and monitored forums to deliver high-fidelity alerts on emerging threats, helping reduce response time and minimize potential impact.
Integrating OSINT into your SIEM enhances visibility by combining internal telemetry with external intelligence. This unified view helps uncover zero-day threats and hard-to-detect vulnerabilities faster.
The Role of OSINT in Social Engineering and Phishing Defense
Phishing and social engineering remain among the most exploited attack vectors in cybersecurity. According to Group-IB’s High-Tech Crime Trends 2025 report, phishing attacks surged by 22% in 2024, with over 80,000 phishing websites identified.
The most targeted industries included logistics (25.3%), travel (20.4%), and internet services (16.4%). What’s more concerning is the rise of AI-powered phishing and deepfake-based social engineering, making these attacks harder to detect and even more convincing.
Many of these campaigns are engineered to exploit human error within seconds of delivery. That’s where OSINT becomes critical, as it surfaces early indicators, exposes attacker infrastructure, and helps teams disrupt these campaigns before damage occurs.
Here’s how OSINT cybersecurity techniques give security teams an edge:
- Monitoring Online Communities
Threat actors frequently coordinate phishing campaigns in dark web marketplaces, Telegram groups, and niche forums. Tracking these discussions uncovers active threat kits and indicators. For instance, Group-IB analysts recently discovered a phishing kit targeting an Indian fintech brand being shared on a private forum. OSINT monitoring enabled the takedown of the infrastructure before launch. - Identifying Malicious Domains
Domain enumeration, WHOIS analysis, and passive DNS monitoring uncover lookalike domains that impersonate trusted brands. Group-IB’s Digital Risk Protection platform flags and neutralizes such phishing pages in real time, reducing dwell time and limiting user exposure. - Enhancing Employee Awareness
Using real phishing lures collected via OSINT improves the effectiveness of training simulations. Employees learn to identify threats based on current tactics, not outdated examples. Simulations powered by real-world intelligence significantly lower click-through rates and increase threat reporting. - Predicting Attack Vectors
Analyzing reused infrastructure, subject lines, and delivery tactics helps identify likely targets within your organization. OSINT enables defenders to anticipate where the next attack might occur, thereby strengthening the most vulnerable points first.
Group-IB’s intelligence-led phishing defense equips organizations to track attacker behavior, dismantle malicious infrastructure, and evolve their defenses with each campaign. With this approach, OSINT becomes a proactive force in strengthening your security posture.
Challenges and Limitations of OSINT Research
OSINT can be highly effective, but using it well requires addressing a few critical challenges. If left unchecked, poor data quality, legal boundaries, and overwhelming volume can all compromise investigations. Here’s a breakdown of security teams’ most common challenges and how Group-IB helps solve them.
Data Overload
There’s more data online than any team can realistically review. Without the correct filtering methods, necessary signals get buried under noise. At Group-IB, we utilise a tested framework, developed by cybersecurity experts, to distinguish relevant intelligence from distractions, ensuring analysts focus solely on what matters.
Inconsistent or Unreliable Data
Public data isn’t always accurate or up to date, and relying on it without verification can lead to false positives. Our tools validate sources and correlate multiple data points before surfacing them as credible threat indicators.
Language Barriers
OSINT investigations often involve content in multiple languages, particularly on global forums or the dark web. Group-IB’s multilingual capabilities and contextual analysis enable teams to interpret data accurately without missing key details.
Legal and Ethical Constraints
OSINT must comply with laws like GDPR and respect individual privacy. We offer clear policies, tools, and training that ensure investigations remain compliant while delivering valuable insights.
Future Trends in OSINT and Cyber Threat Intelligence
Open source intelligence is evolving fast, and the next few years will bring even more innovation in how threats are discovered, analyzed, and acted upon. Here are some key trends shaping the future of OSINT in cybersecurity:
- AI-Powered Intelligence Gathering
Machine learning models are increasingly being used to automate OSINT workflows, filter noise, detect anomalies, and accelerate threat detection with improved precision. - Real-Time Threat Correlation
The move toward real-time processing of open source data will enable security teams to identify risks as they emerge, rather than after damage has been done. - Deeper Integration with Security Platforms
OSINT is being more tightly integrated into SIEM, SOAR, and XDR platforms, providing analysts with a comprehensive view of internal and external threats in one place. - Greater Emphasis on Attribution
There’s a growing focus on mapping digital infrastructure to real-world identities. OSINT tools are now used to detect attacks and to build detailed profiles of threat actors behind them. - Expansion into Non-Traditional Sources
OSINT is shifting toward tracking unconventional data sources, such as Telegram channels, dark web forums, and decentralized platforms, where threat actors operate with minimal oversight. - Visualization and Pattern Recognition Tools
Future OSINT tools will prioritize visual mapping, converting raw data into relationship graphs that enable analysts to connect infrastructure, campaigns, and actor behavior at a glance.
These trends underscore the growing importance of OSINT in effective cybersecurity operations. However, you need the right technology and expertise behind the scenes to maximize its potential.
How Group-IB Turns OSINT Data into Powerful Cybersecurity Insights
OSINT delivers real value when it is deeply integrated into detection, investigation, and response workflows. Public data on its own holds limited value unless it is analyzed in context, connected to relevant threat indicators, and used to inform decisions within a structured cybersecurity framework.
Group-IB’s Unified Risk Platform helps security teams scale OSINT by turning raw public data into prioritized intelligence. It combines real-time threat insights with adaptive risk models to detect external threats early. The platform strengthens your ability to monitor, assess, and respond to evolving risks with greater precision.
Group-IB’s Digital Risk Protection solution provides role-specific dashboards and deep-dive reports tailored to both analysts and business stakeholders to support targeted response efforts. These tools make it easier to investigate brand impersonation attempts, detect exposed credentials, and assess third-party risks with actionable context.
Network Graph, one of Group-IB’s internal investigation tools, supports deeper analysis by consolidating OSINT data from multiple sources and visually mapping connections between threat actors, compromised infrastructure, and exposed digital assets.
We combine data, tools, and analyst expertise to help you translate raw signals into high-confidence intelligence. Schedule a walkthrough to see how our integrated approach can support your security objectives.